In the intricate world of financial markets, the ability to navigate the complex terrain of trading is essential for any investor or trader. Among the plethora of tools and techniques available, trading orders stand out as critical components that can significantly impact a trader’s strategy, risk management, and ultimately, their profits.
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into one of the most essential trading orders – the stop order. Understanding what a stop buy or sell order is, its various types, strategic benefits, potential pitfalls, and real-life examples will empower you to make informed decisions in the dynamic world of trading.
Introduction to the World of Trading Orders
Before we dive into the specifics of what sell stop- orders are, let’s first establish a foundational understanding of trading orders as a whole. In the realm of financial markets, trading orders are essentially instructions given to brokers or trading platforms to execute specific transactions. These orders define the conditions under which a trade is to be executed, taking into account factors like price, timing, and quantity. Understanding the various types of trading orders empowers traders to navigate the markets with precision and agility.
Defining a Stop Order: More Than Just a Command
Stop Order Explained
A stop order is a crucial tool that traders employ to manage risk and protect their investments in the unpredictable world of financial markets. At its core, a stop order is an instruction that becomes executable once a specified price level is reached.
It is designed to limit losses by automatically triggering a market order when the price reaches a predefined point, known as the “stop price.” This means that if the market moves against the trader’s position and maximum price reaches the stop price, the stop order becomes a market order, leading to the execution of the trade.
How a Stop Order Operates in Real-time
Imagine you’re trading a stock that you believe has the potential for substantial gains. However, you’re also cautious about potential losses if the market moves in an unfavorable direction. To protect yourself from significant losses, you can set a stop order with a stop price slightly below the current market price. If the market takes an unexpected downturn and the stock’s price hits your stop price, your stop order becomes a market order, and the trade with sell stop on is executed at the prevailing market price, helping you exit the trade before losses accumulate.
Differentiating Between Stop Order Types
Stop Loss Order: Protecting Your Assets
A stop loss order is perhaps one of the most widely used types of stop orders in trading. Its primary purpose is to protect traders from excessive losses in volatile markets. By setting a stop loss order with a stop price below the entry price sell a stock, traders can ensure that if the market moves against their position, the trade is automatically closed before losses spiral out of control. This type of order is particularly useful for risk-averse traders who prioritize capital preservation.
Stop Limit Order: Combining the Best of Both Worlds
A stop limit order is a variant of the stop order that introduces specified limit price as an additional layer of control. While it shares similarities with the stop loss order, it introduces a limit price along with the stop price. When the stop price is reached, the stop limit order becomes a limit order, and the trade is executed only if the market can be accessed at or better than the limit price. This order offers traders a balance between securing an exit point and achieving a specific price, offering more precise control over trade execution.
Trailing Stop Order: Adjusting to Market Movements
In dynamic markets, where trends can reverse unexpectedly, the trailing stop order shines. Unlike traditional stop orders, which have a fixed stop price, the trailing stop order adjusts as the market price moves in the trader’s favor.
As the market price increases, the trailing stop price moves in tandem with current price move, maintaining a specified distance from the market price. This type of order allows traders to lock in profits while allowing for potential further gains, making it a versatile tool in trending markets.
The Strategic Benefits of Using Stop Orders
The use of stop orders can be a game-changer for traders looking to enhance their risk management and decision-making processes. Here are some strategic benefits that highlight the significance of incorporating stop orders into your trading arsenal:
- Capital Protection: Perhaps the most significant advantage of using stop orders is the protection they provide against unexpected market movements. By setting a stop price, traders can limit potential losses, ensuring that unfavorable price movements do not erode their capital.
- Disciplined Trading: Emotions can often cloud judgment, leading to impulsive decisions. Stop orders act as predetermined exit points, helping traders stick to their trading plans and resist the urge to hold onto losing positions in the hope of a rebound.
- Minimized Monitoring: Financial markets operate 24/7, and constant monitoring can be challenging. Stop orders offer a level of automation, enabling traders to step away from their screens without worrying about missing critical price movements.
- Focus on Strategy: With stop orders in place, traders can focus on analyzing market trends, identifying entry points, and refining their trading strategies. The assurance of risk management allows for a more strategic approach to trading.
Navigating Potential Pitfalls
As with any trading tool, stop orders come with their own set of potential pitfalls that traders must be aware of:
Market Volatility and Early Exits
One challenge traders might encounter is market volatility triggering their stop orders prematurely. In fast-moving markets, prices can momentarily hit the sell stop order in price and then rebound in the intended direction. This can result in the trader exiting the position only to miss out on potential profits as the market corrects itself.
Slippage: Why Execution Price Matters
Slippage refers to the discrepancy between the expected stop price and the actual execution price. During periods of high volatility or low liquidity, the execution of a stop order might occur at a price significantly different from the buy stop order call price. Traders need to factor in slippage when setting their stop prices to ensure that unexpected price variations do not adversely impact their trades.
Tips and Tricks for Effective Stop Order Usage
To make the most of stop orders, traders can adopt the following tips and strategies:
- Volatility Consideration: Volatile markets can lead to rapid price fluctuations. Traders should set stop prices that allow for reasonable market movements while still offering protection.
- Technical Analysis: Utilizing technical analysis can help traders identify suitable stop prices based on support and resistance levels, trendlines, and other key indicators.
- Regular Review: Markets evolve, and a stop price set a while ago might no longer be relevant. Traders should periodically review and adjust their stop orders to align with current market conditions.
- Avoiding Round Numbers: Setting stop prices just above or below round numbers can help traders avoid common stop-hunting practices employed by other market participants.
Diving Into Real-life Examples: Successes and Missteps
Real-life examples illustrate how stop orders can impact trading outcomes, both positively and negatively. Consider a scenario where a trader utilizes a stop loss order to protect their investment in a highly volatile stock. As the stock’s stock price plummets unexpectedly, the stop loss order triggers, limiting the trader’s losses and preserving their capital. This scenario highlights the risk management aspect of stop orders, which can be a saving grace in turbulent markets.
Take a look at this EUR/USD chart. You can see that if you were long of this pair, you could have suffered significant losses if you did not protect profits, or even protect yourself from massive losses. At the blue arrow, you can see that a protective stop loss order to sell would have saved you.
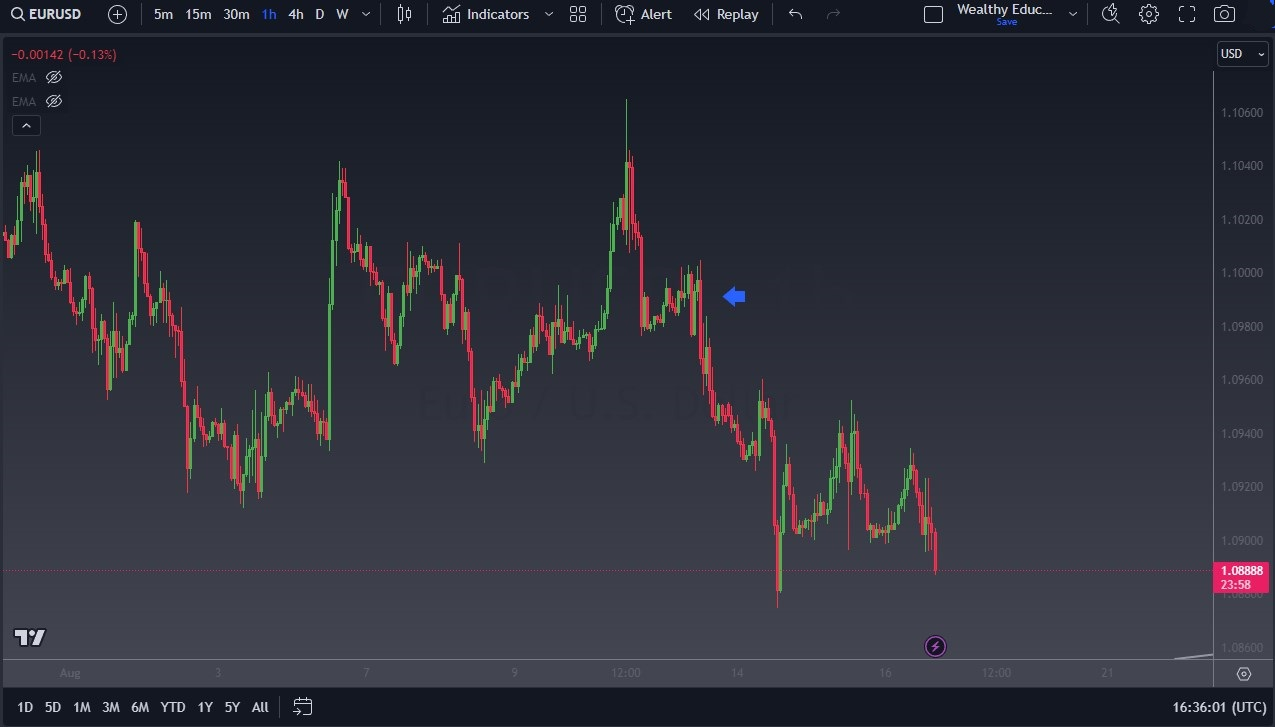
On the flip side, let’s imagine a situation where a trader sets a stop order at a conservative price level in anticipation of a market downturn. However, the market experiences a short-term dip, triggering the stop in order to sell, and causing the trader to exit the position prematurely. Shortly afterward, the market rebounds, missing out on potential gains. This instance underscores the importance of considering market volatility and setting stop prices that align with the trader’s overall strategy.
Conclusion: Mastering Stop Orders for Trading Success
In the realm of trading, the ability to manage risk and protect investments is paramount. Stop orders emerge as indispensable tools that empower traders to navigate the unpredictable waters of financial markets. By understanding the nuances of different types of stop orders, factoring in market volatility, and adopting strategic approaches to setting sell stop orders and prices, traders can harness the power of these orders to enhance their trading endeavors.
Ultimately, mastering the art of stop orders requires a blend of technical knowledge, strategic thinking, and adaptability. Incorporating stop orders into your trading strategy equips you with the ability to secure profits, manage risk, and make informed decisions in the ever-evolving world of finance. As you and sell order and continue your journey as a trader, remember that stop orders are not just commands but powerful instruments that can significantly influence the trajectory of your trading success.
Why would you use a stop order?
A stop order is used to manage risk and protect investments in trading. It automatically triggers a trade when a specified price level (the stop price or sell limit order) is reached. Traders use stop orders to limit potential losses by exciting positions if the market moves against them.
What is a stop order vs limit order?
While both stop orders and limit orders are used in trading, they serve different purposes. A stop order becomes a market order when the stop price is reached, while a limit order becomes executable when the market price reaches a specific limit price or better set by the trader. Stop orders are used to manage risk and execute trades at or near a specific price, while limit orders aim to execute trades at a predetermined price or better.
Are stop orders a good idea?
Yes, stop orders are a valuable tool in trading, particularly for managing risk and protecting investments. They offer traders a level of automation and discipline by automatically executing trades at predefined minimum price and levels. However, it's essential to understand the nuances of different stop order types and consider market conditions before using them to ensure they align with your trading strategy.


