Avalanche is a blockchain that seeks to combine scaling and quick confirmation times through its Avalanche Consensus Protocol. Currently, it is possible to process 4500 transactions per second, compared to just 30 or so for the Ethereum network, which is now trying to increase its speed. Avalanche is considered to be a significant competitor to the Ethereum network.
What Is Avalanche (AVAX)? – Definition & Meaning
Avalanche is a cryptocurrency and blockchain platform that is attempting to be a major rival of Ethereum. The native token, AVAX, uses smart contracts to transfer information and run applications. Avalanche can provide almost instantaneous transaction finality. AVAX is used to pay the transaction processing fees, secure the Avalanche network, and offer a basic unit of accounting among blockchains in the Avalanche ecosystem.
What is the AVAX Token?
AVAX is the native token on the Avalanche Network, used to pay transaction fees, send information, and secure the network. It is a token that runs on its own Layer-1; therefore, security is still paramount, as many Layer-2 solutions run on top of another network, adding another potential security problem.
Ava Labs, Avalanche’s founders, believe they have built the fastest smart contract blockchain to date. AVAX has been among the top 10 cryptos by value as its popularity has skyrocketed.
About AVAX Staking Rewards
Subnets, including the Primary Network on the Avalanche Network, require validators who own and stake AVAX tokens as collateral. Much like other proof-of-stake ecosystems, if you want to receive rewards, you can either become a validator, which is very expensive but earns almost 11% APY, or you can delegate your stake to a validator, which quite often pays more than 9% in rewards.
Avalanche (AVAX) History
Bitcoin was launched in 2009, paving the way for blockchain technology that has come since it, including Ethereum. Since then, innovation has exploded with nonfungible tokens, decentralized finance protocols, and many other applications. Unfortunately, the technical limitations of the original blockchain design have become more apparent.
Along came the idea of a “Layer-2” solution. This was a way to speed up transactions on Ethereum by essentially creating a parallel transaction chain. However, this adds more complexity to the blockchain and, therefore, more potential for security issues.
Ava Labs, the founders of Avalanche, have come up with a three-blockchain solution to address the top problems plaguing the blockchain world. Ava Labs US launched the Avalanche blockchain in September 2020 after raising $6 million during their financing round. Other private and public token sales have amounted to $48 million.
Who Formed Avalanche (AVAX)?
There are three prominent people behind Avalanche: Kevin Sekniqi, Maofan “Ted” Yin, and Emin Gun Sirer. There was a pseudonymous group called Team Rocket which, in May 2018, first released information about the protocol on the Interplanetary File System.
A group of researchers from Cornell developed the technology, led by a professor of computer science and software engineer, Emin Gun Sirer. He was assisted by the other two, who were doctoral students.
In March 2020, the AVA code base for the Avalanche consensus protocol was made available to the public as it became open-source. Avalanche’s ICO, or initial coin offering, ended in July 2020, followed by the launch of the Avalanche Network in September.
How Does Avalanche (AVAX) Work?
Avalanche is composed of three separate blockchains rather than a single one. Each blockchain specializes in a task within the broader Avalanche ecosystem instead of having one chain do everything. This keeps the platform agile, allowing it to achieve decentralization, security, and scalability.
The Exchange Chain (X-Chain)
The Exchange Chain (X-Chain) is a blockchain responsible for creating and the transactions involving Avalanche assets. AVAX, the native token of Avalanche, is the most popular cryptocurrency on the platform, but other decentralized exchange tokens are also popular.
Transactions on the X-Chain generate fees paid in AVAX. It’s similar to how gas fees on Ethereum are paid in ETH, and regardless of what transaction tokens you are using, fees are always settled in AVAX.
The Contract Chain (C-Chain)
The Contract Chain, also known as the “C-Chain,” enables developers to build decentralized applications on Avalanche while leveraging the platform’s security and scalability. Smart contracts are a main feature of Avalanche and live here.
The C-Chain runs smart contracts for the Avalanche platform and is EVM or Ethereum Virtual Machine compatible. Because of this, anybody can deploy Ethereum smart contracts on Avalanche. This allows existing Ethereum apps to deploy a version of their product on Avalanche quickly.
The Platform Chain (P-Chain)
The Platform Chain, also known as the “P-Chain,” enables anyone to create a Layer-1 or Layer-2 blockchain. You can even go so far as to create a group of them. These blockchains are known as “subnets,” with the P-Chain being the default subnet common to all of them.
The P-Chain manages a map of Avalanche subnets by keeping track of validators, but the subnets are also responsible for validating the P-Chain.
Avalanche vs. Ethereum
Avalanche differs from Ethereum in multiple ways. Avalanche has a faster transaction processing time, sitting at 4500 transactions per second, compared to the Ethereum limit of 15. The consensus protocol on Avalanche enables the Avalanche network to validate transactions faster than Ethereum.
Ethereum is much larger, supporting more projects and transactions. However, Avalanche’s superior ability to scale could give it a long-term advantage over Ethereum. Avalanche can transact many transactions in a much shorter amount of time.
How is Avalanche Different from Other Scalable Blockchains?
Avalanche competes with other scalable platforms and interoperable blockchains such as Ethereum, Polygon, Polkadot, and Solana. The problems and solutions these ecosystems are trying to address are all similar, so to understand what makes Avalanche different, we need to look “under the hood.”
The Consensus Mechanism
The consensus mechanism, referred to as Avalanche Consensus, is a significant difference. However, most consensus mechanisms with blockchain these days are unique. Avalanche uses the Snowball Algorithm as its building block. This is a majority decision, which goes round and round and eventually “snowballs” into a consensus.
The Transaction Speed and Finalization Time
The finality time of less than 1 second on Avalanche is a huge difference from many of its competitors. While transactions per speed are one primary metric, you must also understand and factor in the time it takes to guarantee a transaction. Avalanche claims to have one of the fastest time-to-finality speeds on a blockchain.
Decentralization on Avalanche
One of the most prominent features of Avalanche is decentralization. It already has many validators, with 1300 being listed as of April 2022 due to its minimal requirements. As time and the price of AVAX has risen, it is becoming more expensive to become a validator for the network.
Avalanche’s Interoperable Blockchains
Avalanche’s interoperable blockchains are potentially unlimited in number. It’s in direct competition with Polkadot, another project that offers customized and interoperable blockchains. However, Polkadot has limited space that is auctioned off, while Avalanche works with a straightforward subscription fee.
What problems does Avalanche (AVAX) solve?
There are three significant issues that Avalanche attempts to solve, as do most of the blockchains. These include scalability, transaction fees, and interoperability.
Problem One: Scalability vs. decentralization
Blockchains typically struggle to balance scalability and decentralization. When a network has increased activity, it can bog down quite quickly. Bitcoin is an example worth noting, as some transactions had even taken days when the network was heavily congested.
One common way to fight congestion is to make the network more centralized so fewer people have more authority to validate the network activity, allowing higher speeds. Decentralization is critical to blockchain security, so networks must reach a balance.
High fees
One of the most common complaints about larger blockchains, especially Ethereum, is the gas fees, which discourage users from using these blockchains. Competition has helped, but it’s still a structural and technical issue. Ethereum has seen smart contract interactions cost over $100.
Interoperability
Projects and businesses will have their own specific needs when using the blockchain, so interoperability is crucial. In the past, it was necessary to work with Ethereum or another individual blockchain that was not designed to their specific needs. They could also use a private blockchain, but there is a high bar to building your own network from scratch.
Avalanche offers a solution with subnets, which are app-specific blockchains that share the primary network security, speed, and interoperability.
What Are the Advantages of Avalanche (AVAX)?
Avalanche has many features that make it unique and viable as a blockchain solution. These include, but are not limited to:
- Unique Technology: Avalanche has unique and innovative technology. Three interoperable blockchains allow the network to overcome most issues in other ecosystems.
- Scalability and Decentralized: Avalanche accomplishes scale without compromising decentralization, something that few other blockchains can claim.
- Interoperability: Avalanche is interoperable with other blockchains, allowing for more significant adoption, especially with Ethereum-based apps.
- Speed and low fees: Avalanche has transaction speeds of over 4500 per second and features very low transaction fees.
What Are the Disadvantages of Avalanche (AVAX)?
While Avalanche is an impressive blockchain and the ecosystem, not everything is perfect, and there are a few things to keep in the back of your mind, such as:
- Malicious validator behavior is not punishable: On most crypto networks, validators that make mistakes or engage in fraudulent behavior get punished by losing some or all of their stake. However, Avalanche does not do this.
- Avalanche can be expensive to buy: One of the downsides to becoming popular is that AVAX has sometimes gotten quite costly.
- Competition: Competition is a significant problem for most blockchain ecosystems, and Avalanche is no different.
- Validator expense: It can become expensive to become a validator on the AVAX network. You need a minimum of 2000 AVAX tokens.
Is Avalanche (AVAX) a Good Investment?
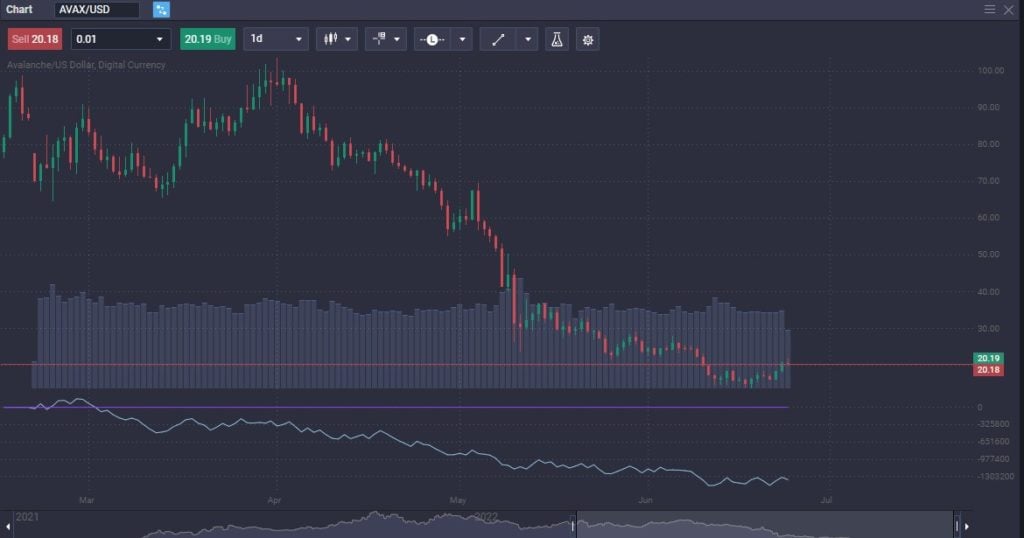
Avalanche has the potential to be an excellent long-term investment. This is mainly because it has a unique architecture, allowing for much more flexibility, scalability, and speed than many other ecosystems. However, the future is wide open regarding crypto, and it is difficult to predict where things may go.
AVAX could find a place in a well-balanced crypto portfolio. If you are a trader, you may be better off trading in the CFD market at a broker like PrimeXBT. This allows you to take advantage of price fluctuations without the hassle of custodial issues or dealing with wallets. A lot of traders will do a little of both.
Conclusion
Avalanche is an exciting project that seems to be growing in popularity and, more likely than not, will find a lot of adoption. However, when it comes to crypto, things are still somewhat up in the air as to how it all shakes out. That said, Avalanche certainly has a good shot at becoming a viable project that lasts for years.
The future looks suitable for blockchain technology, and the unique way Avalanche takes on the three main goals of decentralization, scalability, and security bodes well for the future of Avalanche itself. Whether or not it becomes the “Ethereum killer,” as many people suggested, will be a different conversation altogether, but it certainly looks like it has a strong future.
Is AVAX a good investment?
The Avalanche platform saw massive growth in 2021, culminating in an almost 500% increase in daily transactions. The native cryptocurrency token, AVAX, had gained 3300% at its peak. However, the future is still up in the air, and therefore it should be considered a speculative investment.
What does AVAX crypto do?
AVAX is the native token of the Avalanche platform and is used to power transactions in the ecosystem. It is used to send rewards, participate in governance, and facilitate transactions on the network by paying fees.
What is the AVAX network?
AVAX is the abbreviation for the Avalanche Network. Launched in 2020 by Ava Labs, it is a blockchain platform used to send and receive smart contracts.
Is AVAX better than Ethereum?
AVAX is the primary utility token for the Avalanche ecosystem. It is much faster than Ethereum, which only processes roughly 30 transactions per second but is in the process of upgrading. They both can handle the solidity programming language, so that AVAX may be quicker at this point, but both are racing for the same destination.
How high will AVAX get?
Nobody knows the answer to this question, as it will be dependent on developer adoption, but perhaps more importantly, a “must-have app” hitting the network. That being said, it does seem to have a lot of interest.
How do I use AVAX?
AVAX is used to pay transaction fees and can be staked to secure the network known as “Avalanche.” Avalanche is compatible with Solidity, Ethereum’s programming language. AVAX can be used to send value in a frictionless manner, as well as collateralized assets.
Is AVAX secure?
The Avalanche network has never been breached, and it is open-sourced code that has been audited by multiple security firms and certified as safe. It has more validators than other smart contract platforms, effectively providing users with security well above the 51% industry standard.
What blockchain is AVAX on?
AVAX is on its own blockchain, known as “Avalanche.” It is a major competitor to Ethereum.
Is AVAX proof of work?
No. AVAX is a “proof-of-stake” consensus. This system rewards those who stake their coins on the network with more AVAX as they validate transactions on the blockchain.
Can AVAX be mined?
You don’t mine AVAX, it is staked, and more coins are minted as rewards for those helping validate transactions on the network.
The content provided here is for informational purposes only. It is not intended as personal investment advice and does not constitute a solicitation or invitation to engage in any financial transactions, investments, or related activities. Past performance is not a reliable indicator of future results.
The financial products offered by the Company are complex and come with a high risk of losing money rapidly due to leverage. These products may not be suitable for all investors. Before engaging, you should consider whether you understand how these leveraged products work and whether you can afford the high risk of losing your money.
The Company does not accept clients from the Restricted Jurisdictions as indicated in our website/ T&C. Some services or products may not be available in your jurisdiction.
The applicable legal entity and its respective products and services depend on the client’s country of residence and the entity with which the client has established a contractual relationship during registration.




